A Comprehensive Guide to SAP Functional: Modules, Roles & Benefits
Introduction
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) is a leading enterprise resource planning (ERP) software that helps businesses streamline processes. SAP is divided into functional and technical domains. SAP Functional consultants focus on business processes and how SAP software can optimize them. This guide explores SAP Functional modules, roles, benefits, and career opportunities.
What is SAP Functional?
SAP Functional refers to the application of SAP modules to handle various business operations such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relationships. Functional consultants bridge the gap between business needs and SAP software capabilities by configuring modules to optimize workflows.

Key SAP Functional Mohttps://mentortechsystems.com/sap-sd-s4-hanadules
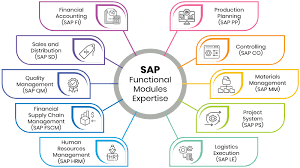
SAP offers various modules designed for different business functions. Below are some of the most important SAP Functional modules:
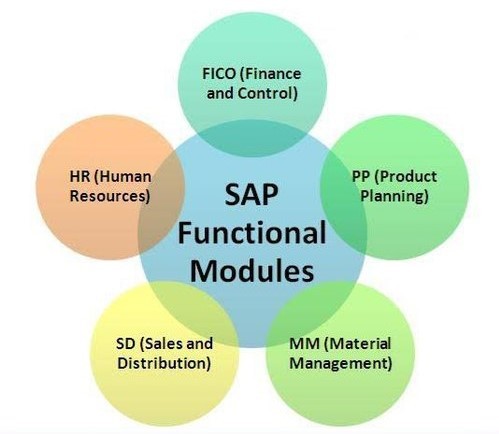
1. SAP FI (Financial Accounting)
SAP FI is used for financial reporting and accounting processes. It helps organizations maintain accurate financial records and comply with regulations.
- Key Features: General Ledger, Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, Asset Accounting.
- Alt Tag: SAP FI module financial accounting features.
2. SAP CO (Controlling)
SAP CO focuses on cost tracking and management within an organization. It helps in budgeting, forecasting, and profitability analysis.
- Key Features: Cost Center Accounting, Profitability Analysis, Internal Orders.
- Alt Tag: SAP CO module for cost management.
3. SAP SD (Sales and Distribution)
SAP SD handles sales, distribution, and billing processes, ensuring smooth order management and customer relationship management.
- Key Features: Order Management, Pricing, Billing, Credit Management.
- Alt Tag: SAP SD module for sales and distribution.
4. SAP MM (Material Management)
SAP MM manages procurement, inventory, and supply chain processes efficiently.
- Key Features: Purchase Orders, Vendor Management, Goods Receipt & Issue.
- Alt Tag: SAP MM module for material management.
5. SAP PP (Production Planning)
SAP PP assists manufacturers in planning and controlling production processes.
- Key Features: Demand Management, Bill of Materials, Capacity Planning.
- Alt Tag: SAP PP module for production planning.
6. SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
SAP HCM helps organizations manage employee data, payroll, recruitment, and performance.
- Key Features: Personnel Administration, Payroll Processing, Time Management.
- Alt Tag: SAP HCM module for human resources.
7. SAP QM (Quality Management)
SAP QM ensures quality control in production and procurement processes.
- Key Features: Quality Inspection, Audit Management, Corrective Action.
- Alt Tag: SAP QM module for quality assurance.
8. SAP PM (Plant Maintenance)
SAP PM helps in maintaining plant equipment, reducing downtime, and improving efficiency.
- Key Features: Preventive Maintenance, Work Order Management.
- Alt Tag: SAP PM module for plant maintenance.
9. SAP CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
SAP CRM enhances customer interactions and relationship management.
- Key Features: Sales Automation, Marketing Campaigns, Customer Service.
- Alt Tag: SAP CRM module for customer relationship management.
10. SAP SCM (Supply Chain Management)
SAP SCM helps organizations optimize logistics and supply chain operations.
- Key Features: Demand Planning, Supplier Collaboration, Transportation Management.
- Alt Tag: SAP SCM module for supply chain optimization.
Roles & Responsihttps://www.facebook.com/mentortechsystemsbilities of an SAP Functional Consultant
SAP Functional consultants are responsible for understanding business requirements and configuring SAP modules accordingly. Key responsibilities include:
- Requirement Analysis: Gather and analyze business needs.
- System Configuration: Customize SAP modules based on requirements.
- Testing & Validation: Conduct unit and integration testing.
- User Training: Train end-users to work efficiently with SAP solutions.
- Support & Maintenance: Troubleshoot issues and implement system upgrades.
Benefits of SAP Functional Implementation
Implementing SAP Functional modules offers several advantages for businesses:
- Improved Efficiency: Streamlines business processes and enhances productivity.
- Data Accuracy: Provides real-time data for informed decision-making.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to financial and legal requirements.
- Scalability: Adapts to business growth and expansion.
- Cost Reduction: Reduces operational costs through process automation.
Career Opportunities in SAP Functional
SAP Functional consultants have a wide range of career opportunities across industries such as finance, manufacturing, retail, and healthcare. Popular SAP Functional career paths include:
- SAP FI/CO Consultant
- SAP SD/MM Consultant
- SAP HCM Consultant
- SAP CRM Consultant
- SAP SCM Consultant
Conclusion
SAP Functional modules play a critical role in enhancing business processes and ensuring operational efficiency. Whether you’re a professional looking for a rewarding career in SAP or a business aiming to optimize workflows, SAP Functional offers immense value. Understanding the different modules, roles, and benefits can help organizations and individuals make the most of SAP ERP.